· Dave Brewster (dave@augustdata.ai) · rag · 5 min read
RAG: How do you configure retrieval?
Part 3: How is RAG retrieval configured in Eidolon.
This is Part 3 of a 3 part series on Retrieval-Augmented Generation.
For general information on RAG, see Part 1: Define RAG and its components.
For information on configuring RAG storage in Eidolon, see Part 2: How is RAG storage configured in Eidolon..
In the last post, we discussed how to configure RAG storage in Eidolon. In this post, we will discuss how to configure retrieval in Eidolon. Retrieval is the process of selecting a set of document fragments from a vector database that are relevant to the current context. The retrieved fragments are then used to generate a response. Retrieval is a key component of the RAG model, and is responsible for providing the model with the information it needs to generate coherent and informative responses.
RAG Retrieval Process
In a basic RAG process, the retrieval component is responsible for selecting a set of document fragments from a vector database that are relevant to the current context or query. The retrieval process is typically performed using a nearest neighbor search algorithm, which finds the document fragments that are closest to the query vector in the vector space. The retrieved fragments are then passed to the generation component, which uses them to augment the search context.
While this process works, it doesn’t return the most relevant information. To improve the quality of the retrieval process, we can use a more sophisticated retrieval process that either augments the query with additional information, generates multiple queries based on the original query, or both. Research is ongoing in this area, and new techniques are being developed to improve the quality of the retrieval process.
In Eidolon, the retrieval process is implemented using the builtin RetrievalAgent. All parts of the retrieval process are handled by the RetrievalAgent and each part is pluggable.
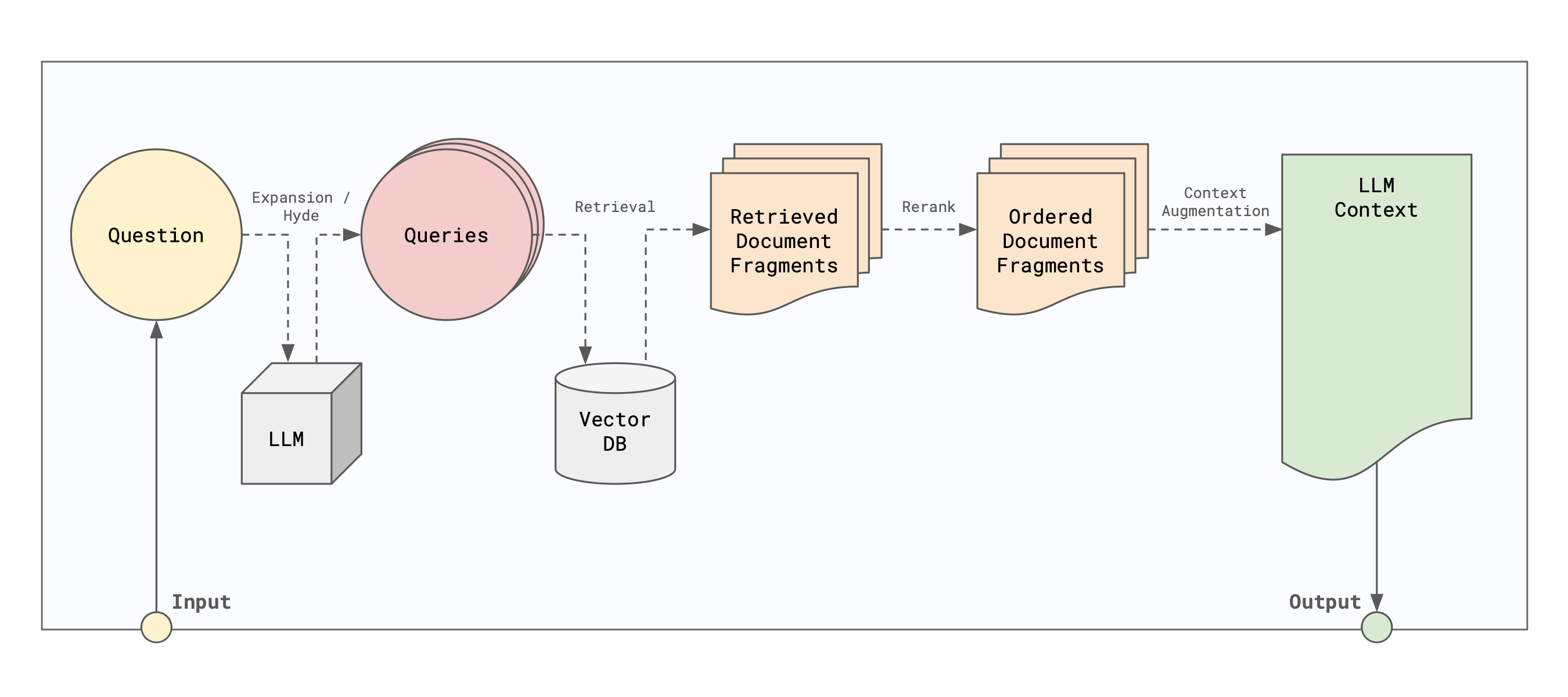
Eidolon implements retrieval by breaking it down into the following steps:
- Query rewrite / expansion
- Document Retrieval
- Document Re-ranking
- Result summarization
Query Rewrite / Expansion
The first step in the retrieval process is to rewrite or expand the original query to improve the quality of the retrieved documents. This can be done using a variety of techniques, such as expanding the query with other information from the context or database or writing multiple queries based on the original query. The goal of this step is to improve the quality of the retrieved documents by providing the retrieval algorithm with more information to work with.
The default implementation is MultiQuestionTransformer which takes the original query and generates multiple queries based on the original query using the configured apu.
Document Retrieval
The next step in the retrieval process is to retrieve a set of document fragments from the vector database that are relevant to the queries. The default implementation uses the AgentOS registered embedding model to embed each query and then uses the vector database to find the most similar documents.
Document Re-ranking
The next step in the retrieval process is to re-rank the retrieved documents to improve the quality of the results. This can be done using a variety of techniques, such as re-ranking the documents based on their relevance to the query or re-ranking the documents based on their similarity to the context. The goal of this step is to improve the quality of the retrieved documents by providing the retrieval algorithm with more information to work with.
The default implementation is RAGFusionReranker which takes a list of document fragments and scores and re-ranks them based on the scores.
Result Summarization
The final step in the retrieval process is to summarize the retrieved documents to provide the generation model with a concise representation of the information. This can be done using a variety of techniques, such as summarizing the documents based on their relevance to the query or summarizing the documents based on their similarity to the context. The goal of this step is to provide the generation model with a concise representation of the information that is relevant to the query.
The default in ResultSummarizer takes a list of document fragments and returns a pointer to the original document as well as the fragment of the document that was retrieved.
Each of these steps is implemented as a separate component that can be swapped out for a different implementation. This allows you to customize the retrieval process to fit your specific use case.
The spec for the RetrievalAgent is as follows:
class RetrieverSpec(BaseModel): max_num_results: int = Field(default=10, description="The maximum number of results to consider.") question_transformer: AnnotatedReference[QuestionTransformer] document_retriever: AnnotatedReference[DocumentRetriever] document_reranker: AnnotatedReference[DocumentReranker] result_summarizer: AnnotatedReference[ResultSummarizer]Each of the components above represents a step in the retrieval process.
The RetrievalAgent is usually used as an agent in conjunction with other agents when retrieval of information from a vector database is needed. You rarely use it directly as it would produce confusing results to the user. In standard search applications, you would front the RetrievalAgent with a copilot agent that interacts with the user, using the RetrievalAgent as a secondary agent to search for information.
Conclusion
The RAG retrieval process is a key component of the RAG model and is responsible for selecting a set of document fragments from a vector database that are relevant to the current context. The retrieval process is implemented in Eidolon using the RetrievalAgent, which handles all parts of the retrieval process and allows you to customize each step to fit your specific use case. Each step in the retrieval process is implemented as a separate component that can be swapped out for a different implementation, allowing you to customize the retrieval process to fit your specific use case.